How to Extend Windows Server 2022 Evaluation Period: A Step-by-Step Guide

Introduction
If you’re running Windows Server 2022 and your evaluation period is about to end, you might be wondering how to extend it. Extending the evaluation period allows you to continue using the server while planning for a full license purchase or upgrade. This guide will walk you through the process of extending your Windows Server 2022 evaluation period, including using various tools and commands.
Understanding the Windows Server 2022 Evaluation Period
What is the Windows Server 2022 Evaluation Period?
The Windows Server 2022 evaluation period is a trial phase that allows users to test the features and capabilities of the server before making a purchase. This period typically lasts for 180 days.
Why Extend the Evaluation Period?
Extending the evaluation period gives you more time to assess the server’s functionality and compatibility with your infrastructure before committing to a full license.
Preparing for the Extension
Check Your Current Evaluation Status
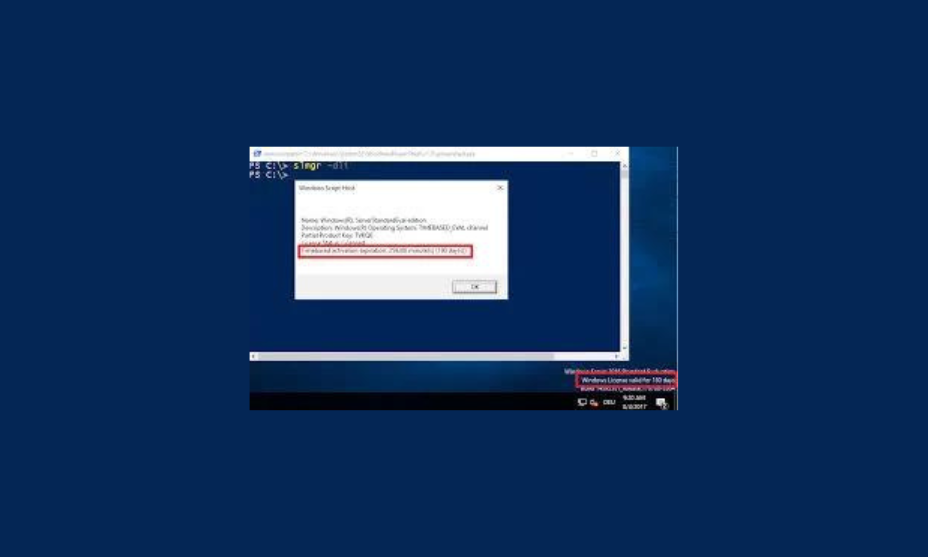
Before extending, it’s crucial to check how much time remains in your current evaluation period. Use the Command Prompt or PowerShell to view this information.
slmgr.vbs /dli
Backup Your Server
Always backup your server data and configurations before making changes to avoid any loss in case of unexpected issues.
Extending the Evaluation Period
Using Command Prompt
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator:
- Right-click the Start button and select Command Prompt (Admin) or Windows Terminal (Admin).
- Run the Command:
- To extend the trial period, use the following command:
slmgr.vbs /rearm
- This command resets the evaluation period, granting an additional 180 days.
- Restart Your Server:
- After running the command, restart your server to apply the changes.
Using PowerShell
- Open PowerShell as Administrator:
- Right-click the Start button and choose Windows PowerShell (Admin).
- Execute the Extension Command:
- Similar to Command Prompt, use the following PowerShell command:
powershellslmgr /rearm
- Reboot Your Server:
- Restart the server for the new evaluation period to take effect.
Additional Steps and Considerations
Licensing Tools and Server Management
- Server Manager and Licensing Tools can also be used to monitor and manage your server’s evaluation status. Check the server settings to ensure all configurations are correct.
Activation Process and License Management
- If you plan to purchase a full license, start the activation process before the extended period expires. Navigate to Settings > Update & Security > Activation to enter your license key.
Handling Remote Desktop Services (RDS)
- For servers using Remote Desktop Services (RDS), ensure that the extension does not affect your RDS licensing. Review your RDS configuration and licensing grace period.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
License Expiration Issues
If you encounter issues with license expiration or reactivation, ensure that you are using the correct commands and that your server configurations are up-to-date.
Evaluation Upgrade
In some cases, an evaluation upgrade might be necessary. This involves transitioning from an evaluation version to a fully licensed version without reinstalling the server.
Managing Windows Server 2022 Licensing
Understanding Server Licensing
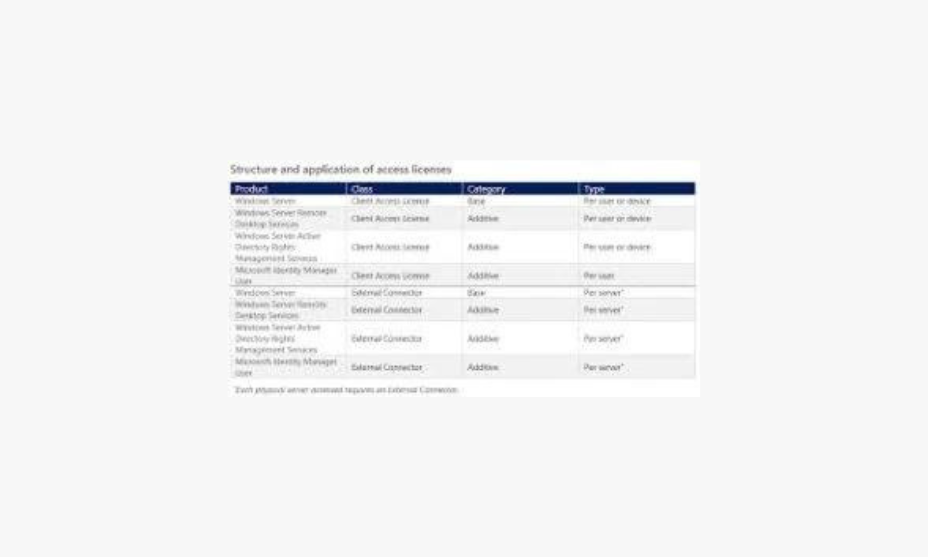
Windows Server 2022 licensing involves purchasing a valid license key to activate the server beyond the evaluation period. There are various licensing options available, including standard, data center, and essentials editions, each tailored to different needs.
How to Purchase a License
- Visit the Microsoft Store:
- Go to the Microsoft Store and choose the appropriate Windows Server 2022 license.
- Select Your Edition:
- Choose the edition that best fits your requirements (Standard, Datacenter, etc.) and complete the purchase.
- Receive License Key:
- After purchase, you will receive a license key via email or directly from the store.
Activating Windows Server 2022
Activation Process
- Open Activation Settings:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Activation.
- Enter License Key:
- Click on Change product key and enter the license key you received.
- Activate Server:
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the activation process.
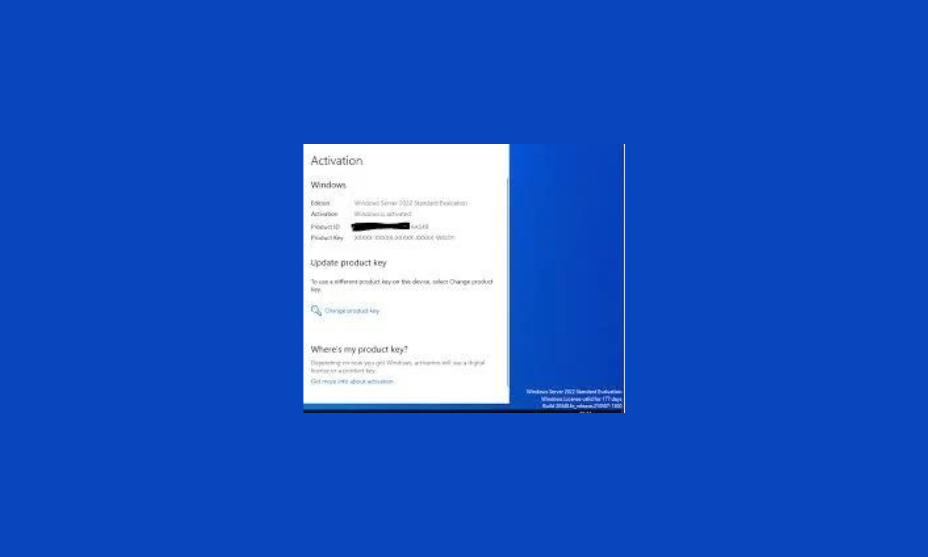
Verification
- After activation, ensure that the server shows as activated in the Activation Settings. You should see a message confirming that Windows is activated.
License Management Best Practices
Regular License Reviews
- Periodically review your license status to ensure compliance and to manage any upcoming renewals or changes in your licensing needs.
Using Licensing Tools
- Utilize Licensing Tools in Windows Server to track and manage licenses effectively. Tools like SLMGR and PowerShell can provide detailed information about your current licensing status.
Document Your License Key
- Keep a record of your license key and purchase information in a secure location. This can be useful for troubleshooting and future reference.
Handling License Expiration and Renewal
Grace Period and Renewal Options
- Windows Server 2022 provides a licensing grace period if your license is about to expire. During this time, you can renew your license without interruption to your server’s operation.
Reactivating Windows Server
- Check License Status:
- Use Command Prompt or PowerShell to check your license status and determine if reactivation is needed.
- Reactivation Commands:
- If necessary, use the following command in Command Prompt to reactivate:
slmgr.vbs /ato
- In PowerShell, you can use:
powershellslmgr /ato
- Troubleshooting:
- If reactivation fails, check for common issues like incorrect license key entries or network connectivity problems.
Utilizing PowerShell for License Management
PowerShell Commands for Licensing
- Get License Information:
slmgr /dli- Display Activation Status:
powershellslmgr /xpr
Automating License Management
PowerShell scripts can be used to automate the monitoring and management of licenses, ensuring that your server remains compliant with licensing requirements.
Advanced Tips and Best Practices
To maximize the efficiency and reliability of your Windows Server 2022 setup, implementing advanced strategies and best practices is essential. This section provides insights into optimizing server performance, ensuring compliance, and maintaining a secure environment.
Optimizing Server Performance
Regular Updates and Patches
- Enable Automatic Updates:
- Ensure that automatic updates are enabled to keep your server updated with the latest security patches and performance improvements.
- Apply Patches Regularly:
- Regularly check for and apply updates manually if automatic updates are not feasible. This helps address vulnerabilities and bugs.
Performance Tuning
- Monitor Resource Usage:
- Use Performance Monitor or Task Manager to keep an eye on CPU, memory, and disk usage. This helps identify and address any bottlenecks.
- Optimize Services:
- Disable unnecessary services and applications to free up system resources. how to extend windows server 2022 evaluation period Focus on services that are critical for your server’s operation.
- Adjust Power Settings:
- Configure power settings to High Performance to ensure that the server operates efficiently under load.
Ensuring Compliance and Security
Regular Backups
- Implement a Backup Strategy:
- Regularly back up your server data and system configurations. Use tools like Windows Server Backup or third-party solutions for automated backups.
- Test Backups:
- Periodically test backup restorations to ensure that your data can be recovered in case of a failure or disaster.
Security Best Practices
- Configure Firewalls:
- Use Windows Defender Firewall or a third-party firewall to control inbound and outbound traffic and protect against unauthorized access.
- Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
- Assign roles and permissions based on user needs to limit access to sensitive data and critical server functions.
- Enable BitLocker:
- Use BitLocker to encrypt server drives and protect data from unauthorized access, especially if the server is portable or at risk of physical theft.
Managing Server Configurations
Document Your Server Settings
- Maintain Documentation:
- Keep detailed records of your server configurations, settings, and any changes made. This aids in troubleshooting and future server management.
- Use Configuration Management Tools:
- Tools like System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) can help manage and automate configuration settings across multiple servers.
Automation with PowerShell
- Create Automation Scripts:
- Develop PowerShell scripts to automate routine tasks such as backups, updates, and system monitoring. This reduces manual effort and ensures consistency.
- Schedule Regular Tasks:
- Use Task Scheduler to automate scripts and tasks, such as server maintenance or performance monitoring, at regular intervals.
Handling Licensing Grace Periods and Expirations
Monitor License Status
- Regular License Checks:
- Regularly check the status of your license using Command Prompt or PowerShell to avoid unexpected expiration issues.
- Plan Ahead for Renewals:
- Schedule reminders for license renewals to ensure that you address any licensing issues before the grace period ends.
Reactivation Procedures
- Prepare for Reactivation:
- Have your license key and activation details ready. Follow the reactivation steps outlined earlier to ensure smooth operation.
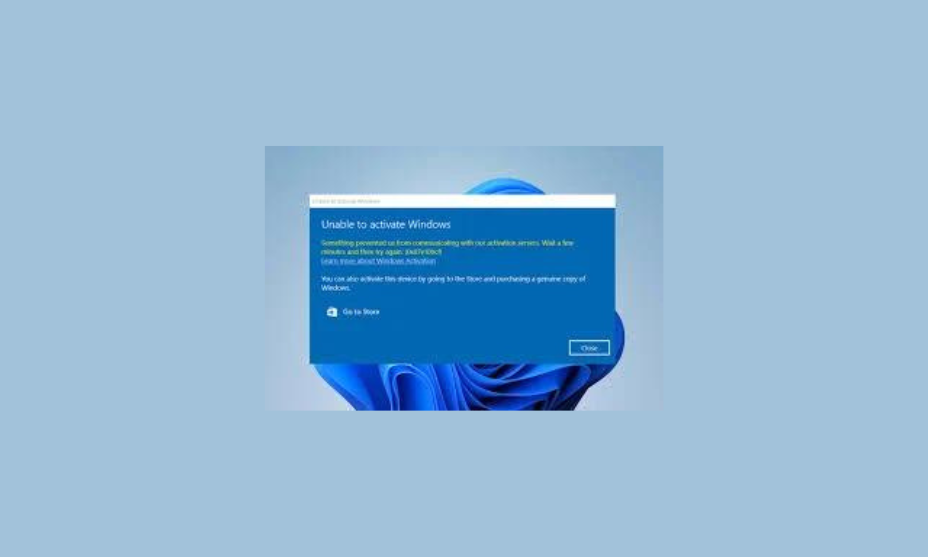
- Address Activation Failures:
- If reactivation fails, check for network issues, key entry errors, or contact Microsoft support for assistance.
Advanced Troubleshooting
Diagnosing Performance Issues
- Use Resource Monitor:
- Resource Monitor provides detailed insights into resource usage and helps pinpoint performance issues.
- Analyze Event Logs:
- Check Event Viewer for warnings and errors related to system performance or application failures.
Resolving Licensing Issues
- Check Activation Errors:
- Review error codes and messages during activation and use Microsoft’s online resources or support for resolution.
- Consult Documentation:
- Refer to Microsoft’s official documentation for detailed guidance on resolving specific licensing or activation issues.
Future-Proofing Your Server Infrastructure
To ensure that your Windows Server 2022 setup remains effective and adaptable as technology evolves, it’s crucial to plan for future needs and advancements. This section will guide you through strategies to future-proof your server infrastructure, including planning for upgrades, scaling your setup, and adopting emerging technologies.
Planning for Upgrades
Regular Assessment of Server Needs
- Evaluate Current Usage:Regularly assess your server’s performance and resource usage. Determine if the server meets your current needs or if you require additional resources.
- Forecast Future Requirements:Anticipate future growth and changes in your organization’s IT requirements. Plan for upgrades based on projected increases in workload and data.
Upgrading to Newer Versions
- Stay Informed About New Releases:Keep track of upcoming releases and updates for Windows Server. Microsoft frequently updates its server software with new features and improvements.
- Plan Upgrade Paths:Develop a strategy for upgrading to newer versions of Windows Server or other technologies. Consider factors such as compatibility, licensing, and training.
- Test Upgrades in a Staging Environment:Before deploying an upgrade to your production environment, test it in a staging environment to identify potential issues and ensure compatibility.
Scaling Your Server Setup
Horizontal vs. Vertical Scaling
- Horizontal Scaling (Scaling Out):
- Add more servers to distribute the load. This approach can improve performance and reliability by balancing workloads across multiple servers.
- Vertical Scaling (Scaling Up):
- Upgrade the existing server’s hardware (CPU, memory, storage) to handle increased demands. Vertical scaling can be simpler but may have limitations based on hardware capabilities.
Cloud Integration
- Leverage Cloud Services:
- Integrate with cloud services such as Microsoft Azure for additional resources and flexibility. Cloud services can complement your on-premises setup and provide scalability.
- Hybrid Cloud Solutions:
- Consider a hybrid cloud approach that combines on-premises servers with cloud resources for greater scalability and disaster recovery options.
Adopting Emerging Technologies
Embracing Virtualization
- Implement Virtual Machines (VMs):
- Use virtualization technologies like Hyper-V to create multiple virtual servers on a single physical server. Virtualization can improve resource utilization and reduce hardware costs.
- Explore Containerization:Adopt container technologies such as Docker to deploy and manage applications in isolated environments. Containers offer flexibility and efficiency in application deployment.
Adopting Automation and AI
- Automate Routine Tasks:Implement automation tools and scripts to streamline routine server management tasks. Automation reduces manual effort and minimizes errors.
- Leverage AI and Machine Learning:Explore AI and machine learning solutions for predictive maintenance, performance optimization, and enhanced security.
Enhancing Security Measures
- Implement Advanced Security Features:Utilize features like Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) and Microsoft Sentinel for enhanced security and threat detection.
- Regular Security Audits:Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential security gaps.
Managing Server Lifecycles
Lifecycle Management
- Track Hardware and Software Lifecycles:
- Keep track of the lifecycle of your server hardware and software to plan for replacements and updates before they reach end-of-life.
- Establish a Replacement Schedule:
- Develop a replacement schedule for outdated hardware and software to maintain optimal performance and security.
Documentation and Knowledge Management
- Maintain Comprehensive Documentation:Keep detailed documentation of your server configurations, changes, and updates. This information is valuable for troubleshooting and future upgrades.
- Invest in Training:Ensure that your IT team is well-trained and up-to-date with the latest technologies and best practices. Training helps in effectively managing and evolving your server infrastructure.
Conclusion
By implementing these advanced tips and best practices, you can optimize the performance, security, and management of your Windows Server 2022 environment. Regular monitoring, effective use of tools, and adherence to best practices will help you maintain a robust and compliant server setup.
FAQs, how to extend windows server 2022 evaluation period
1. What is the default evaluation period for Windows Server 2022?
The default evaluation period for Windows Server 2022 is 180 days. After this period, the server will enter a reduced functionality mode unless extended or activated with a valid license.
2. Can the evaluation period of Windows Server 2022 be extended?
Yes, you can extend the evaluation period of Windows Server 2022 multiple times using the “slmgr” command. This can extend the evaluation by an additional 180 days, up to a maximum of 5 extensions.
3. How do I check how many days are left in the current evaluation period?
You can check the remaining evaluation period by running the following command in an elevated Command Prompt window.
4. How do I extend the evaluation period of Windows Server 2022?
To extend the evaluation period, follow these steps:
Open an elevated Command Prompt (Run as Administrator).
Type the following command and press Enter:bash
Copy code Restart your server after executing the command. This will reset the evaluation period, providing an additional 180 days.
5. How many times can I extend the Windows Server 2022 evaluation period?
You can extend the evaluation period up to five times, which gives you a total possible evaluation period of 3 years (5 * 180 days = 900 days).
6. What happens after I run out of extensions for the evaluation period?
After you have used all five rearm attempts, you will no longer be able to extend the evaluation period. At this point, you will need to activate the server with a valid license to continue using it without restrictions.
7. Can I upgrade from the evaluation version to a full version of Windows Server 2022?
Yes, you can upgrade from the evaluation version to a fully licensed version of Windows Server 2022. This can be done by entering a valid product key through the activation settings or by using the “slmgr” command.
8. What are the limitations of running Windows Server 2022 in evaluation mode?
While running in evaluation mode, you have full access to all features of Windows Server 2022. However, once the evaluation period expires, the server will enter a reduced functionality mode, which restricts certain features and services until activated.
9. Can I extend the evaluation period without restarting the server?
No, extending the evaluation period requires a restart of the server. The extension will not take effect until the system has been rebooted.
10. Will I lose data or configurations when extending the evaluation period?
No, extending the evaluation period using the “slmgr /rearm” command will not affect your data or server configurations. It only resets the evaluation countdown.