The Five Pillars of Cybersecurity: A Comprehensive Guide

Introduction
Cybersecurity is no longer an option but a necessity in today’s digitally interconnected world. Whether you’re a business owner, IT professional, or just someone concerned with personal data, understanding The Five Pillars of Cybersecurity is essential. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental elements, offering a holistic approach to securing information, networks, and systems.
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity refers to the practices, technologies, and processes designed to protect computer systems, networks, and data from cyber threats, attacks, and unauthorized access. As our reliance on technology increases, cybersecurity becomes essential for safeguarding sensitive information from cybercriminals and malicious entities.
How Cybersecurity Works
Cybersecurity operates through a combination of technologies and best practices aimed at protecting various aspects of information systems. Here’s how it typically works:
- Protection Layers: Cybersecurity involves multiple layers of security measures, such as firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems.
- Risk Assessment: Organizations conduct regular assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential risks to their systems and data.
- Data Encryption: Sensitive information is often encrypted to make it unreadable to unauthorized users.
- Access Controls: Strict access controls ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data and systems.
- Monitoring and Response: Continuous monitoring of networks helps detect unusual activities, allowing for quick response to potential threats.
- Training and Awareness: Organizations often conduct training programs to educate employees about cybersecurity best practices and how to recognize threats like phishing attacks.
The 5 Pillars of Cybersecurity
Confidentiality
- Objective: Protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or disclosure.
- Explanation: Confidentiality ensures that only authorized individuals or systems can access sensitive information. Encryption, access controls, and strong authentication mechanisms (such as passwords or biometrics) are commonly used to safeguard data. For example, when you log into a banking app, only you can access your account details, and the data is encrypted to prevent theft during transmission.
Integrity
- Objective: Ensure the accuracy and trustworthiness of data.
- Explanation: Data integrity means that information remains unaltered during storage or transmission unless changed through authorized processes. This pillar protects against unauthorized modifications, ensuring that data is reliable. Techniques like hashing and digital signatures help verify that data has not been tampered with. In business, maintaining integrity is crucial for processes such as financial transactions, where even small errors or malicious changes can have significant impacts.
Availability
- Objective: Ensure that information and resources are available to authorized users when needed.
- Explanation: Availability focuses on keeping systems and data accessible at all times, especially during critical operations.
- Denial of service (DoS) attacks, hardware failures, or software bugs can jeopardize availability. To counteract these, organizations use redundancy, load balancing, and backup systems to maintain uptime. For example, e-commerce websites invest in robust server infrastructure to ensure availability during high-traffic events like sales.
Authentication
- Objective: Verify the identity of users or systems accessing data or systems.
- Explanation: Authentication ensures that the entity trying to access a system is who or what they claim to be. This pillar includes measures such as usernames, passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and biometrics (e.g., fingerprint or facial recognition). By requiring users to prove their identity through multiple steps, cybersecurity systems reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Non-repudiation
- Objective: Ensure that an individual or system cannot deny having performed a certain action.
- Explanation: Non-repudiation means that users cannot deny their actions, such as sending a message or approving a transaction. This pillar is enforced using mechanisms like digital signatures and audit logs. These tools provide proof of action, which is particularly important in legal and financial scenarios. For example, digital contracts signed with cryptographic signatures ensure that the signer cannot later deny their involvement.
Incorporating these pillars into cybersecurity strategies helps organizations create robust defenses against a wide range of cyber threats, including data breaches, attacks, and fraud. Together, they ensure the protection, reliability, and accessibility of information in both personal and professional environments.
Features of Cybersecurity
- Data Protection: Safeguarding sensitive data from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Network Security: Protecting the integrity and usability of networks.
- Application Security: Ensuring software and applications are secure from vulnerabilities.
- Endpoint Security: Protecting individual devices connected to the network.
- Incident Response: Developing and implementing strategies to respond to security breaches or attacks.
- Compliance: Adhering to laws and regulations governing data protection and privacy.
Pros and Cons of Cybersecurity
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Protects Sensitive Data: Safeguards personal and business information from theft and breaches. | Costly Implementation: Establishing and maintaining robust cybersecurity measures can be expensive. |
| Reduces Risk of Cyber Attacks: Helps in minimizing the chances of successful cyberattacks. | Complexity: Implementing effective cybersecurity can be complex and require specialized knowledge. |
| Increases Customer Trust: Customers feel more secure when their data is protected, enhancing brand reputation. | False Sense of Security: Some organizations may become complacent, believing they are fully protected when they may not be. |
| Compliance with Regulations: Helps organizations meet legal and regulatory requirements for data protection. | User Friction: Security measures may hinder user experience or productivity if not implemented effectively. |
| Continuous Monitoring: Provides ongoing surveillance to detect and respond to threats in real-time. | Evolving Threat Landscape: Cyber threats are constantly evolving, requiring continuous updates and vigilance. |
Information Security: Protecting Data Integrity
Information security is the foundation of cybersecurity, focusing on the protection of data from unauthorized access, disclosure, or disruption. It ensures confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA) of data, often referred to as the CIA triad.
Key Elements of Information Security:
- Confidentiality: Ensuring only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data.
- Integrity: Safeguarding the accuracy and reliability of data.
- Availability: Ensuring data is accessible to authorized users when needed.
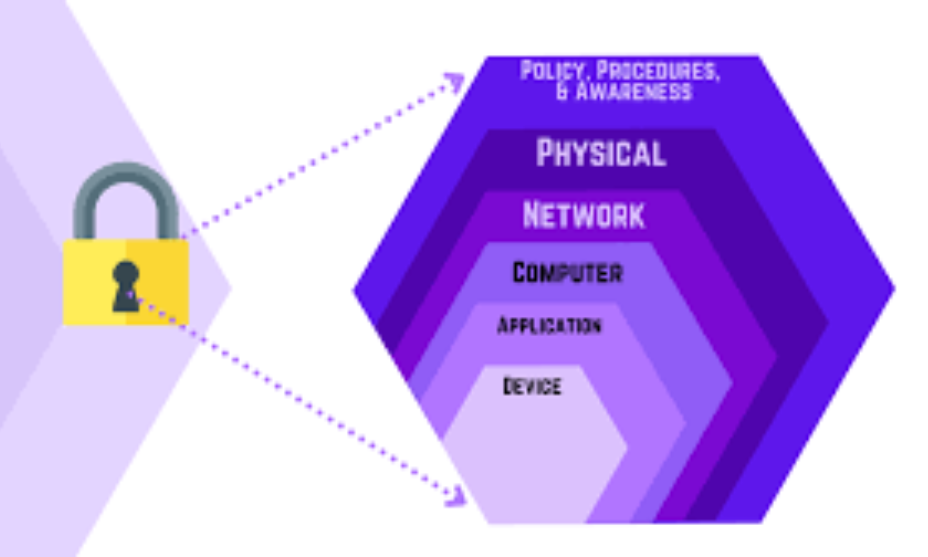
Network Security: Defending the Infrastructure
Network security is essential to protect the underlying infrastructure of computers and systems. It involves implementing measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and VPNs to secure internal networks from threats.
Key Aspects of Network Security:
- Firewall: A critical security tool that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic.
- Zero Trust Architecture: A security model requiring all users to be authenticated and authorized before accessing data or applications.
The 5 Pillars of Cybersecurity form the foundation of effective information security practices, providing a comprehensive approach to protect systems, networks, and data. These pillars focus on different areas of security to ensure confidentiality, integrity, availability, and resilience of information systems. Here’s an overview of each pillar:
Application Security: Securing Software at the Source
Applications are often the target of cyberattacks. Therefore, application security focuses on safeguarding software from threats during development and deployment. Secure coding practices, penetration testing, and regular updates are crucial for minimizing vulnerabilities.
Best Practices in Application Security:
- Input Validation: Ensuring that user-provided data cannot exploit software vulnerabilities.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data to protect it during transmission and storage, making it unreadable to unauthorized individuals.
Risk Management: Identifying and Mitigating Threats
Cybersecurity risks are constantly evolving, and it’s crucial to identify potential vulnerabilities through risk management processes. This includes assessing the potential impact of threats and implementing safeguards to reduce risk.
Steps in Cybersecurity Risk Management:
- Risk Assessment: Regularly identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities within the system.
- Vulnerability Assessment: A more detailed inspection of weaknesses that could be exploited by cybercriminals.
Incident Response: Handling Security Breaches
Even the most secure systems can face breaches, which makes having an incident response plan crucial. This pillar is about the systematic approach to managing and mitigating the consequences of a cybersecurity attack.
Key Steps in Incident Response:
- Detection and Analysis: Identifying the breach and understanding its scope.
- Containment: Limiting the damage to prevent further infiltration.
- Recovery: Restoring normal operations as quickly as possible.
Cybersecurity Strategies: Beyond the Five Pillars
While the five pillars offer a robust framework, additional cybersecurity strategies like security awareness training and business continuity plans play a significant role in a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy.
Security Awareness Training:
Employee education is vital in preventing common cyber threats like phishing attacks. Regular training helps employees recognize threats and respond appropriately.
Business Continuity Plan:
A business continuity plan ensures that the organization can continue operating during and after a cyberattack, minimizing downtime and data loss.
In-Depth Strategies for Enhancing Cybersecurity in Your Organization
To take your cybersecurity efforts to the next level, it’s essential to develop a proactive and layered approach. Beyond the basic principles outlined in the Five Pillars of Cybersecurity, organizations can implement a range of advanced strategies to strengthen their defense mechanisms and reduce vulnerabilities.
Adopting a Zero Trust Architecture
In traditional network security models, once users are inside the network, they’re often granted trust to access various systems. However, the Zero Trust model assumes no user or device should be trusted by default, regardless of their location.
Key Components of Zero Trust:
- Micro-segmentation: Dividing the network into smaller segments to limit the damage from a breach.
- Least Privilege Access: Ensuring users and systems only have access to the data and resources necessary for their role.
- Continuous Authentication: Constantly validating users and devices as they move through the network.
Zero Trust helps mitigate insider threats and external attacks by reducing lateral movement within the network.
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Passwords alone are no longer sufficient to secure sensitive systems and data. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to access systems.
Benefits of MFA:
- Stronger Security: Even if a password is compromised, an attacker cannot access the system without the additional factor.
- User-Friendly Solutions: Modern MFA tools, like biometric authentication and one-time passcodes, are easy to implement and use.
Conducting Regular Security Audits
A cybersecurity strategy is never complete without ongoing assessments. Regular security audits help to identify new vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards.
Types of Security Audits:
- Internal Audits: Performed by in-house teams to assess current systems and policies.
- Third-Party Audits: External experts can provide an unbiased assessment of your security posture.
- Penetration Testing: Ethical hacking to simulate cyberattacks and find vulnerabilities before attackers do.
- Enhancing Data Encryption Protocols
With the rise of data breaches, encryption has become a non-negotiable part of cybersecurity. Encrypting data both at rest and in transit ensures that sensitive information remains secure even if accessed by unauthorized individuals.
Types of Encryption:
- Symmetric Encryption: The same key is used for both encryption and decryption.
- Asymmetric Encryption: Uses a public and private key pair, providing stronger protection for sensitive transactions and communications.
Ensure that all critical data is encrypted, especially for sensitive communications like financial transactions and personal data.
Developing a Robust Incident Response Plan
As cyberattacks become more sophisticated, it’s not a matter of if, but when a breach will occur. A well-prepared incident response plan ensures that your organization can quickly contain and recover from an attack, minimizing damage.
Key Components of an Incident Response Plan:
- Preparation: Identifying and training a response team.
- Detection and Analysis: Setting up systems to detect and analyze threats in real-time.
- Containment: Isolating affected systems to prevent the attack from spreading.
- Eradication and Recovery: Removing the threat and restoring normal operations.
Regular drills and updates to the plan ensure preparedness and minimize downtime during real incidents.
Implementing Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
With more employees working remotely, protecting endpoints such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets has become crucial. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools continuously monitor endpoints for suspicious activity and automatically respond to potential threats.
Benefits of EDR:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Detects abnormal behavior on endpoints instantly.
- Automated Responses: Many EDR solutions can isolate compromised devices and alert administrators to prevent the spread of an attack.
- Comprehensive Reporting: EDR provides detailed logs and reports to aid in post-incident analysis and improve security posture.
Creating a Cybersecurity Awareness Program
Human error remains one of the leading causes of cybersecurity incidents. Educating your staff about security best practices and how to recognize potential threats can significantly reduce the risk of a breach.
Elements of an Effective Awareness Program:
- Phishing Simulations: Train employees to recognize phishing emails by running simulated attacks.
- Regular Training Sessions: Cover topics like password hygiene, recognizing malware, and handling sensitive data.
- Company-Wide Policies: Ensure every employee is familiar with your organization’s cybersecurity policies and incident reporting procedures.
Strengthening Cloud Security Measures
As businesses continue to migrate to the cloud, cloud security must be a priority. While cloud service providers offer security features, organizations still need to implement their own strategies to ensure data and applications are protected.
Cloud Security Best Practices:
- Data Encryption: Ensure all data stored and transferred in the cloud is encrypted.
- Access Control: Implement strong access management policies to limit who can access sensitive data.
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up data stored in the cloud to recover from accidental deletions or ransomware attacks.
Protection Against Cyber Threats
The five pillars of data protection
- Confidentiality ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive information, preventing data breaches and unauthorized exposure.
- Non-repudiation guarantees that the sender and recipient cannot deny their actions, ensuring accountability and transparency in data exchanges.
- Authenticity verifies that users and systems interacting with the data are who they claim to be, preventing unauthorized access or impersonation.
- Integrity maintains the accuracy and consistency of data, protecting it from tampering or unauthorized modification.
- Availability ensures that data remains accessible to authorized users when needed, preventing downtime or loss of critical information.
Together, these pillars form a comprehensive strategy to protect data from external threats and internal vulnerabilities, ensuring its security, accuracy, and accessibility in any organization.
Understanding current cyber trends is crucial for individuals and organizations alike, as it helps to stay informed about the evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats and practices. Here’s a breakdown of some key trends currently shaping the field:
Rise of Ransomware Attacks
- Ransomware continues to be one of the most significant threats, targeting both large enterprises and small businesses. Attackers encrypt data and demand a ransom for its release, often using advanced techniques to bypass traditional security measures.
Increased Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- AI is being utilized both by attackers, who automate attacks and enhance phishing schemes, and by defenders, who use machine learning to detect anomalies and predict potential threats more effectively.
Remote Work Security Challenges
- The shift to remote work has increased vulnerabilities, as employees access corporate networks from various locations and devices. This trend has led to a rise in attacks on unsecured home networks and personal devices.
Zero Trust Architecture
- Organizations are increasingly adopting a zero trust model, which assumes that threats could be internal or external. This approach emphasizes strict identity verification and access controls, regardless of the user’s location.
Supply Chain Attacks
- Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting supply chains to compromise larger organizations through their vendors. These attacks can have widespread effects, as seen in incidents like the SolarWinds breach.
Cloud Security Concerns
- With the migration to cloud services, concerns about data privacy, compliance, and security are rising. Organizations are focusing on securing their cloud environments and understanding the shared responsibility model.
Increased Regulation and Compliance
- Governments are enacting stricter regulations regarding data protection (like GDPR and CCPA), pushing organizations to enhance their cybersecurity measures and ensure compliance to avoid penalties.
Phishing and Social Engineering Tactics
- Cybercriminals are refining their phishing tactics, making them more sophisticated and convincing. Employees are often targeted through social engineering to gain access to sensitive information or systems.
Internet of Things (IoT) Vulnerabilities
- The proliferation of IoT devices presents new security challenges. Many IoT devices have weak security protocols, making them attractive targets for attackers looking to gain a foothold in larger networks.
Focus on Cyber Resilience
- Organizations are not only investing in prevention but also in recovery strategies. Cyber resilience emphasizes the ability to recover quickly from attacks and maintain essential functions in the face of disruption.
Which five components are necessary for cyber security?
To combat such threats, secure sensitive data, and maintain business continuity, a range of cyber security techniques are used. Constructing a strong cybersecurity framework may be made more organized by having a thorough understanding of the five Cs of cybersecurity: change, continuity, cost, compliance, and coverage.
Conclusion
Understanding and implementing the Five Pillars of Cybersecurity is essential in safeguarding digital assets from potential cyber threats. Whether it’s information security, network security, or incident response, every aspect plays a vital role in creating a resilient cybersecurity strategy. Additionally, incorporating continuous risk management and application security measures ensures your systems remain secure against evolving threats.
By following these principles, organizations and individuals alike can bolster their defenses and respond more effectively to cyber threats. Prioritizing cybersecurity not only protects data but also builds trust and credibility in today’s digital landscape.
FAQs, five pillars of cybersecurity
1. What are the five pillars of cybersecurity?
The five pillars of cybersecurity are generally defined as Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability, Authentication, and Non-repudiation. These principles help protect data, systems, and networks from cyber threats.
2. What is confidentiality in cybersecurity?
Confidentiality ensures that sensitive information is accessed only by authorized users. It is achieved through encryption, access controls, and data classification systems to protect against unauthorized access.
3. How does integrity support cybersecurity?
Integrity ensures that data remains accurate and unaltered during storage or transmission. Mechanisms such as cryptographic hashes and version control help detect unauthorized changes to data.
4. What is the role of availability in cybersecurity?
Availability ensures that systems, applications, and data are accessible to authorized users when needed. Measures like redundancy, backups, and disaster recovery plans are used to maintain availability during attacks or system failures.
5. Why is authentication critical in cybersecurity?
Authentication verifies the identity of users, devices, or systems before granting access to sensitive information. Methods include passwords, biometrics, two-factor authentication, and digital certificates.