The Future of Cloud Computing: Exploring Cloudspace Technologies

Introduction
Cloud computing has evolved significantly over the years, becoming a critical element of modern business infrastructure. As we move towards a more digitized future, cloudspace technologies continue to play a pivotal role in transforming the way companies manage, store, and process data.
This article delves deep into the future of cloud computing, focusing on key trends, emerging technologies, and how businesses can leverage cloudspace solutions for growth.
Overview of Cloud Computing
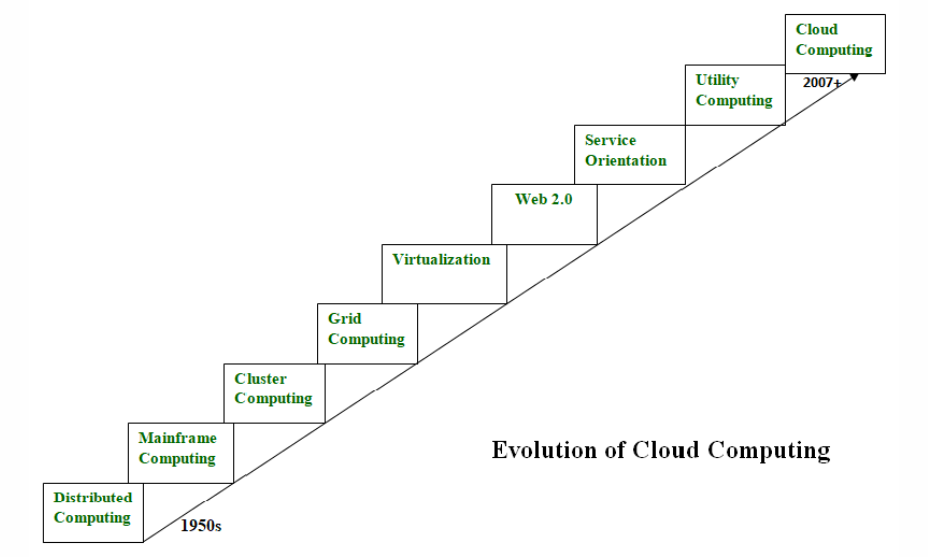
Evolution of Cloud Computing
Evolution of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has dramatically transformed how businesses and individuals store, process, and manage data. Its evolution can be traced through several key phases:
- Early Foundations (1960s-1990s): The concept of cloud computing dates back to the 1960s, when computer scientist John McCarthy proposed the idea of computation as a utility. In the 1990s, the rise of the internet set the stage for cloud-based services.
- Virtualization and Grid Computing (Early 2000s): Virtualization technologies allowed servers to host multiple systems, leading to more efficient use of resources. The Future of Security Grid computing, which linked computer networks for shared computing power, also laid the groundwork for the modern cloud.
- Rise of Cloud Service Providers (Mid-2000s): Companies like Amazon (with AWS), Google, and Microsoft began offering cloud services, allowing users to access storage and computing power on demand. These services introduced the concepts of Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) and Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS).
- Widespread Adoption (2010s): Businesses and individuals embraced cloud computing for its flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. Bedrock Computer Technologies (SaaS) applications like Dropbox, Gmail, and Salesforce became popular.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Solutions (Late 2010s-Present): Today, cloud computing has evolved into complex architectures with hybrid clouds (mixing private and public clouds) and multi-cloud strategies. These systems offer better control, security, and flexibility for enterprises.
- Emerging Trends: The future of cloud computing includes advancements in edge computing, AI integration, and serverless architectures, making cloud services even more integral to digital transformation.
Overall, the evolution of cloud computing has revolutionized IT infrastructure, enabling businesses to be more agile and competitive in the digital era.
The Role of Cloudspace in Modern Digital Transformation
Key Benefits of Adopting Cloud Technologies
- Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduce upfront infrastructure costs and pay for what you use.
- Accessibility: Remote access to data and applications.
- Flexibility: Choose between public, private, or hybrid cloud environments.
- Security: Enhanced data protection through encryption and compliance standards.
Pros and Cons of cloud computing:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Cost Efficiency | Security Risks |
| Reduces the need for physical hardware and maintenance costs. | Data breaches and unauthorized access can be a concern. |
| Scalability | Downtime |
| Easily scalable resources based on demand. | Service outages can affect access to services. |
| Accessibility | Limited Control |
| Access data and applications from anywhere with internet connectivity. | Users may have less control over infrastructure and data management. |
| Automatic Updates | Vendor Lock-In |
| Software updates and maintenance are handled by the provider. | Difficulty in migrating data and services between different cloud providers. |
| Disaster Recovery | Internet Dependency |
| Improved data backup and recovery options. | Requires a reliable internet connection to access services. |
This table provides a clear overview of the main advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing.
Understanding Cloudspace Technologies
Traditional vs. Cloudspace Solutions
Traditional IT infrastructure relies heavily on physical hardware and localized data centers, while cloudspace technologies offer virtualized, distributed environments that are more flexible, scalable, and efficient.
Types of Cloud Computing Services
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, including servers, storage, and networking. Companies can rent these resources on-demand, making it a popular choice for organizations that need to manage complex IT workloads.
Use Cases for IaaS:
- Hosting websites and web applications
- Storing large amounts of unstructured data
- Running high-performance computing tasks
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers a platform for developers to build, test, and deploy applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. This speeds up development and enables teams to focus on coding rather than managing hardware.
Use Cases for PaaS:
- Building scalable web applications
- Automating software development processes
- Simplifying application deployment
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for companies to install and maintain software on individual machines. It is commonly used for office productivity tools, customer relationship management (CRM), and email services.
Use Cases for SaaS:
- Collaboration tools like Google Workspace
- CRM software like Salesforce
- Email marketing platforms like Mailchimp
key features of cloud computing:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| On-Demand Self-Service | Users can provision computing resources automatically without human intervention. |
| Broad Network Access | Services are accessible over the network via standard mechanisms from various devices (e.g., smartphones, tablets, laptops). |
| Resource Pooling | Multiple users share the same physical resources, which are dynamically allocated and reassigned as needed. |
| Rapid Elasticity | Resources can be scaled up or down quickly to meet demand, providing a flexible environment. |
| Measured Service | Resource usage is monitored, controlled, and reported, providing transparency for both the provider and the consumer. |
| Multi-Tenancy | Multiple customers share the same physical infrastructure while keeping their data isolated and secure. |
| Automatic Updates | Service providers manage updates and patches, ensuring that users always have the latest features and security measures. |
| High Availability | Cloud services are designed to be available and reliable, often with backup and disaster recovery options in place. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces the need for upfront capital expenditures, allowing businesses to pay only for what they use. |
| Security | Providers often implement robust security measures to protect data, including encryption and access control. |
Emerging Trends in Cloud Computing
The Rise of Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies
Businesses are increasingly adopting hybrid and multi-cloud strategies to optimize their cloud deployments. A hybrid cloud integrates both on-premises infrastructure and cloud services, while a multi-cloud strategy involves using services from multiple cloud providers. These approaches offer flexibility, cost optimization, and risk mitigation by avoiding vendor lock-in.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning in Cloud Services
AI and machine learning are now integral components of cloudspace technologies, offering capabilities such as automated data analysis, predictive maintenance, and intelligent cloud management. This trend is reshaping industries by providing faster, data-driven decision-making.
Installing cloud computing services
Installing cloud computing services involves several steps, typically focused on setting up cloud infrastructure or utilizing cloud service platforms. Here’s a brief overview:
- Choose a Cloud Provider: Select a cloud service provider (CSP) like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), or IBM Cloud.
- Create an Account: Sign up for an account on the chosen platform. This usually requires providing some personal or business information.
- Select a Service Model:
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): Offers hardware and software tools over the internet.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis.
- Set Up the Environment:
- Choose a Region: Select a data center region based on latency and compliance needs.
- Configure Resources: Set up virtual machines, storage, databases, or other resources needed for your application.
- Network Configuration: Set up networking options, including Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs), subnets, and security groups to manage access.
- Deploy Applications: Upload and configure your applications, services, or websites on the cloud infrastructure.
- Monitoring and Management: Utilize tools provided by the cloud service for monitoring performance, scaling resources, and managing costs.
- Security and Compliance: Implement security measures such as firewalls, encryption, and access controls to protect data.
Each cloud provider has specific documentation and tools that assist with installation, so refer to the respective guides for detailed instructions.
The Role of Edge Computing in Cloudspace Technologies
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing refers to processing data closer to where it is generated rather than relying on centralized cloud servers. It reduces latency, enhances real-time data processing, and minimizes bandwidth usage.
Edge Computing Applications
- Smart Cities: Enabling real-time traffic management and public safety monitoring.
- IoT Devices: Improving the performance of connected devices by reducing response times.
- Healthcare: Real-time patient monitoring and remote surgeries.
Cloud Security and Compliance
Key Challenges in Cloud Security
Despite the numerous advantages, cloud computing presents significant security challenges, including:
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Lack of Visibility: Difficulty in tracking data movement across cloud environments.
- Compliance Issues: Meeting industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2.
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Protection
- Data Encryption: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA for an extra layer of security.
- Regular Audits: Conduct security audits to ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Key Features of Cloudspace Technologies You Need to Know
Scalability:
Cloudspace Technologies offers highly scalable cloud solutions, allowing businesses to expand or reduce resources based on their needs without over-committing to infrastructure.
Security:
With advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits, Cloudspace Technologies prioritizes data protection and compliance with industry standards.
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Capabilities:
Cloudspace enables seamless integration across private, public, and hybrid cloud environments, allowing businesses to manage workloads across multiple platforms efficiently.
Cost Efficiency:
Through pay-as-you-go models and optimized resource management, Cloudspace Technologies helps businesses control costs by paying only for the services they actually use.
Automation:
Cloudspace offers automated infrastructure management tools, reducing manual workloads and improving overall operational efficiency.
Global Data Centers:
With data centers located around the globe, Cloudspace ensures low latency, faster data processing, and reliable service delivery, no matter the geographical location.
AI and Machine Learning Integration:
Cloudspace Technologies provides integrated AI and machine learning tools, helping businesses automate processes, analyze large datasets, and derive valuable insights.
Disaster Recovery:
Cloudspace provides robust disaster recovery solutions to ensure continuous availability and quick recovery of critical data in case of unexpected disruptions.
Developer-Friendly Tools:
Cloudspace Technologies offers a suite of developer-friendly tools like APIs, SDKs, and DevOps integrations, making cloud application development and deployment easier.
These key features make Cloudspace Technologies a flexible, secure, and efficient solution for businesses looking to harness the power of cloud computing.
Cloudspace Technologies for Small and Medium Businesses: Benefits and Solutions
Cloudspace Technologies offers tailored cloud solutions that are ideal for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). By leveraging Cloudspace’s flexible infrastructure, SMBs can scale their operations without the need for heavy investments in physical hardware.
Key Benefits:
- Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go models reduce upfront costs and allow businesses to scale resources based on demand.
- Scalability: SMBs can easily scale up or down as their needs change, ensuring they only pay for what they use.
- Data Security: Advanced security features like encryption and regular backups help protect sensitive business data.
- Remote Accessibility: Cloudspace enables employees to access files and applications from anywhere, promoting flexibility and remote work.
- Disaster Recovery: Built-in backup and recovery solutions minimize downtime in case of data loss or system failures.
Solutions Offered:
- Cloud Storage: Affordable storage options to manage growing data needs.
- Managed Services: Cloudspace handles IT infrastructure, freeing up time for businesses to focus on core operations.
- Collaboration Tools: Cloud-based collaboration platforms enhance team productivity.
- Top Industries Benefiting from Cloudspace Technologies
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery with Cloudspace Technologies
Overview: Cloudspace Technologies offers comprehensive data backup and disaster recovery solutions designed to safeguard critical business data against loss, corruption, or disasters. These solutions ensure that organizations can quickly recover their data and maintain continuity in operations.
Key Features:
- Automated Backups:
- Cloudspace Technologies provides automated backup solutions that regularly back up data without manual intervention. This minimizes the risk of human error and ensures data is always up-to-date.
- Flexible Recovery Options:
- Organizations can choose from various recovery options, including full system restores, individual file recovery, or point-in-time restores, allowing for tailored recovery strategies based on specific needs.
- Secure Storage:
- Data is stored in secure, off-site locations, ensuring that it is protected against physical threats such as fires, floods, or theft. Encryption methods are employed to safeguard data during transmission and at rest.
- Rapid Recovery Time:
- With advanced recovery solutions, Cloudspace Technologies aims to minimize downtime, ensuring that businesses can restore operations swiftly and efficiently after a disaster.
- Scalability:
- The backup solutions are scalable, allowing businesses to adjust their storage needs as they grow. This ensures that organizations only pay for what they use while maintaining flexibility.
- Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS):
- Cloudspace Technologies offers DRaaS solutions, enabling businesses to replicate their critical systems in the cloud. This ensures that, in the event of a disaster, they can quickly switch operations to a backup site.
- Regular Testing:
- To ensure effectiveness, regular testing of backup and disaster recovery plans is conducted. This helps organizations identify potential weaknesses and ensures that recovery procedures work as intended.
- Compliance and Reporting:
- Cloudspace Technologies provides compliance solutions that adhere to industry regulations. Detailed reporting and auditing features help businesses maintain oversight of their backup and recovery processes.
Benefits:
- Business Continuity: Ensures that businesses can continue operations with minimal disruption after a data loss event.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces the costs associated with data loss, including potential fines, lost revenue, and damage to reputation.
- Peace of Mind: Organizations can focus on core business activities, knowing their data is secure and recoverable.
Understanding Cloudspace Technologies’ Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) Offerings by Cloudspace Technologies:
Cloudspace Technologies provides a robust suite of SaaS solutions that allow businesses to access software applications over the internet without the need for complex infrastructure or costly installations. Their SaaS offerings cover a wide range of business functions, from customer relationship management (CRM) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) to collaboration tools and project management platforms.
The key benefit of Cloudspace’s SaaS solutions is easy scalability—businesses can quickly expand their usage based on need, paying only for what they use. Moreover, the software is constantly updated and maintained by Cloudspace, ensuring security, reliability, and compliance with the latest standards. This helps businesses reduce IT overhead costs while staying agile in an evolving digital landscape.
Cloudspace’s SaaS products are user-friendly, come with integrated data security, and offer real-time collaboration features, making them ideal for both small and large enterprises aiming to streamline operations and improve productivity.
Cloudspace Technologies’ Approach to Cloud Compliance and Governance
focuses on ensuring that businesses meet regulatory requirements while maintaining data security and transparency. They implement a robust framework that adheres to international standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2, enabling clients to stay compliant across different regions.
Their governance model includes automated policy enforcement, real-time monitoring, and auditing tools that track data usage, access controls, and security protocols. Cloudspace Technologies also offers customizable compliance solutions, allowing businesses to tailor security measures to meet industry-specific regulations, ensuring both flexibility and accountability in cloud operations.
Cloudspace Technologies for Developers: Tools and Resources
Cloudspace Technologies offers a comprehensive suite of tools and resources tailored specifically for developers, enabling them to build, deploy, and manage applications efficiently in the cloud. These tools support various programming languages, frameworks, and environments, giving developers flexibility in their workflow.
Key offerings include:
- API Integration: Cloudspace provides robust APIs for seamless integration, allowing developers to connect their applications with cloud services effortlessly.
- Developer SDKs: Ready-made SDKs in popular programming languages like Python, Java, and Node.js simplify the development process.
- DevOps Tools: Cloudspace supports continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, helping developers automate code testing, deployment, and monitoring.
- Scalability Features: Developers can leverage auto-scaling options to manage growing workloads without manual intervention.
- Documentation and Tutorials: A rich library of technical documentation, tutorials, and community forums is available to help developers get started quickly and troubleshoot any issues.
These tools and resources empower developers to create scalable, secure, and efficient cloud-based applications with ease.
How Cloudspace Technologies Simplifies Cloud Migration
Cloudspace Technologies streamlines the complex process of migrating data, applications, and infrastructure to the cloud through automated tools and step-by-step guidance. Their migration solutions are designed to minimize downtime and data loss by ensuring seamless transitions with minimal disruption to ongoing operations.
The platform supports a wide range of cloud environments (private, public, and hybrid), making it easier for businesses to shift workloads without needing to reconfigure systems. Cloudspace Technologies also offers expert support, robust security measures, and performance monitoring during and after the migration process, helping companies scale efficiently and securely in the cloud.
5G and Cloud Computing
5G, the fifth generation of mobile network technology, offers significantly higher speeds, lower latency, and greater connectivity compared to its predecessors. Its integration with cloud computing is poised to revolutionize various sectors by enhancing how data is processed, transmitted, and utilized.
Enhanced Speed and Performance
5G networks provide ultra-fast data transfer rates, allowing cloud applications to operate with remarkable efficiency. Users can access cloud services almost instantaneously, improving overall performance and user satisfaction.
Reduced Latency
One of the most significant advantages of 5G is its low latency, often under 10 milliseconds. This reduction is crucial for real-time applications, such as gaming, video conferencing, and remote surgeries, where delays can be detrimental.
Edge Computing Integration
5G facilitates the growth of edge computing by enabling data processing closer to the source of data generation. This means less data needs to be sent to centralized cloud servers, reducing latency and improving response times for applications like autonomous vehicles and smart sensors.
Improved IoT Connectivity
5G enhances the capabilities of the Internet of Things (IoT) by allowing millions of devices to connect simultaneously to the cloud without compromising performance. This leads to smarter homes, cities, and industries where data flows seamlessly between devices and cloud systems.
Real-Time Data Processing
With the capabilities of 5G, cloud services can process vast amounts of data in real time. This is essential for applications in various fields, including finance (for real-time trading) and healthcare (for immediate patient monitoring).
Support for AI and Machine Learning
5G can significantly boost cloud-based AI and machine learning applications by providing the necessary bandwidth for processing large datasets quickly. This enables more sophisticated analytics and faster decision-making.
Cloud Gaming Revolution
5G is transforming the gaming industry by enabling cloud gaming services that deliver high-quality, low-latency gaming experiences without the need for expensive hardware. Players can stream games directly from the cloud, making gaming more accessible.
Enhanced Security Measures
While 5G presents new security challenges, it also offers improved security protocols. Cloud service providers are adapting to leverage these enhancements, ensuring data protection during transmission.
Future Implications
The ongoing integration of 5G and cloud computing will continue to drive innovation across various sectors. Businesses can expect improved operational efficiency, new service offerings, and the ability to harness advanced technologies like AI, big data, and augmented reality.
Exploring Cloud Marketplaces: Opportunities and Challenges
Introduction to Cloud Marketplaces
Cloud marketplaces are online platforms that allow users to buy, sell, and manage cloud-based applications and services. They serve as a central hub for cloud service providers (CSPs) to offer their solutions to a wide audience, making it easier for businesses to find and integrate various tools into their operations.
Opportunities in Cloud Marketplaces
- Increased Accessibility
- Cloud marketplaces provide a centralized location for businesses to discover and purchase cloud solutions, making technology more accessible to organizations of all sizes.
- Wide Range of Solutions
- Users can access a variety of services, from Software as a Service (SaaS) applications to Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offerings, allowing for flexible solutions tailored to specific needs.
- Simplified Procurement
- Streamlined purchasing processes enable organizations to quickly acquire the tools they need without extensive vendor negotiations or lengthy implementation times.
- Enhanced Visibility for Vendors
- Cloud marketplaces give service providers greater exposure to potential customers, allowing them to reach a broader audience and potentially increase sales.
- Integration with Existing Systems
- Many cloud marketplaces offer solutions that easily integrate with existing cloud services, facilitating smoother transitions and enhanced functionality.
- Cost-Effective Solutions
- Competitive pricing in cloud marketplaces can lead to cost savings for businesses, as they can compare different offerings and choose the best fit for their budgets.
Challenges in Cloud Marketplaces
- Market Saturation
- The growing number of offerings can lead to market saturation, making it difficult for businesses to differentiate between products and choose the best solution.
- Quality Assurance
- Not all products in cloud marketplaces meet the same quality standards. Users may face challenges in identifying reliable vendors and high-quality solutions.
- Security and Compliance Risks
- The integration of third-party services introduces potential security vulnerabilities and compliance issues, requiring businesses to conduct thorough assessments before adoption.
- Vendor Lock-In
- Businesses may become dependent on specific vendors, leading to challenges if they want to switch providers or migrate away from certain services.
- Complexity of Integration
- While many solutions promise easy integration, the reality can be more complex, often requiring technical expertise and additional resources.
- Limited Support
- Some cloud marketplaces may not offer sufficient customer support, leaving users without adequate assistance when issues arise.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Cloud Technologies
Cloud Computing for Remote Work: Trends and Technologies
As remote work becomes a permanent fixture in many organizations, cloud computing has emerged as a crucial enabler, providing the flexibility and tools necessary for teams to collaborate effectively from anywhere. Here’s a look at key trends and technologies shaping this landscape:
Increased Adoption of Cloud Services
- Trend: Organizations are increasingly migrating their operations to cloud-based platforms to facilitate remote work. This shift allows for scalable resources and improved accessibility.
- Technologies: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) are commonly used cloud models.
Collaboration Tools
- Trend: The demand for effective collaboration tools has surged, enabling teams to communicate and share information seamlessly.
- Technologies: Platforms like Microsoft Teams, Zoom, and Slack provide video conferencing, chat, and document sharing capabilities, enhancing teamwork across distances.
Virtual Desktops and Remote Access Solutions
- Trend: Organizations are deploying virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) solutions, allowing employees to access their work environments from any device.
- Technologies: Services like Amazon WorkSpaces and Citrix Virtual Apps enable secure, remote access to desktops and applications.
Enhanced Security Measures
- Trend: With the increase in remote work, there’s a heightened focus on cybersecurity to protect sensitive data accessed over cloud platforms.
- Technologies: Multi-factor authentication (MFA), Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), and endpoint security solutions are critical for safeguarding remote connections.
Cloud Storage Solutions
- Trend: Businesses are utilizing cloud storage to ensure that employees have access to necessary files and documents from any location.
- Technologies: Services like Google Drive, Dropbox, and Microsoft OneDrive offer scalable storage options and collaborative features.
Automation and Workflow Optimization
- Trend: Automation tools are becoming essential for managing workflows and increasing productivity in remote teams.
- Technologies: Cloud-based solutions such as Zapier and Microsoft Power Automate help streamline processes by integrating various applications.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
- Trend: Organizations are leveraging AI to improve productivity and decision-making in remote work environments.
- Technologies: Cloud providers like AWS and Google Cloud offer AI and machine learning services that can enhance data analysis and automate repetitive tasks.
Focus on Employee Well-Being
- Trend: Companies are increasingly prioritizing employee well-being and work-life balance in remote work policies.
- Technologies: Wellness platforms integrated into cloud services help track employee engagement and mental health.
Cloud Computing in Healthcare: Future Innovations
Cloud computing is set to revolutionize the healthcare industry by enhancing data accessibility, improving patient care, and enabling innovative solutions. Here’s a detailed look at the future innovations in this area:
Enhanced Data Storage and Accessibility
- Cloud computing allows healthcare providers to store vast amounts of data securely and access it from anywhere, facilitating better collaboration among medical professionals. This is crucial for patient care, especially in emergency situations.
Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring
- The integration of cloud technology in telemedicine enables healthcare providers to offer remote consultations and monitor patients’ health through connected devices. This innovation improves access to care, especially in rural and underserved areas.
Big Data Analytics
- Cloud computing supports big data analytics in healthcare, allowing providers to analyze large datasets to uncover insights related to patient outcomes, disease trends, and treatment effectiveness. This can lead to more personalized medicine and improved healthcare policies.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- AI and machine learning algorithms can be deployed in cloud environments to enhance diagnostic accuracy, predict patient outcomes, and streamline administrative tasks. These technologies can analyze patterns in patient data, leading to better decision-making.
Interoperability and Data Sharing
- Cloud computing promotes interoperability between different healthcare systems, enabling seamless data sharing among providers. This leads to comprehensive patient records, improving coordination of care and reducing duplication of tests.
Cost Reduction and Efficiency
- By leveraging cloud solutions, healthcare organizations can reduce infrastructure costs associated with on-premises data centers. Cloud services offer scalable solutions, allowing organizations to pay only for what they use and allocate resources more efficiently.
Disaster Recovery and Data Security
- Cloud providers offer robust disaster recovery solutions, ensuring that critical health data is backed up and can be restored quickly in case of data loss or cyberattacks. Enhanced security measures, including encryption and access controls, protect sensitive patient information.
Mobile Health Applications
- Cloud computing supports the development of mobile health applications that empower patients to manage their health proactively. These applications can track vital signs, medication adherence, and appointment reminders, fostering patient engagement.
Clinical Trials and Research
- Cloud technology streamlines the process of managing clinical trials by enabling efficient data collection and analysis. Researchers can access real-time data from various sources, accelerating the development of new treatments and therapies.
Future Considerations
- As healthcare continues to evolve, future innovations in cloud computing may include advancements in personalized medicine, genomic data analysis, and the integration of augmented and virtual reality for training and patient engagement.
The Future of Cloud Computing
Predictions for Cloudspace Technologies in the Next Decade
The future of cloud computing is set to be dominated by serverless computing, cloud-native development, and API integration. As more businesses move to the cloud, we will see an increased reliance on cloud-native applications and solutions designed to optimize digital infrastructure.
Preparing for Future Advancements
Businesses must stay ahead of the curve by adopting flexible, scalable cloud solutions and investing in technologies like DevOps and containers to enhance their cloud deployments.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Success Stories Leveraging Cloudspace Technologies
- Netflix: Transitioned from data centers to AWS to ensure scalable content delivery across the globe.
- Dropbox: Moved from its data centers to the cloud to enhance collaboration features and reduce storage costs.
Lessons Learned from Cloud Journeys
- Scalability is Key: Businesses that plan for scalability can meet customer demands more efficiently.
- Security Cannot Be Overlooked: Cloud migration comes with security risks, making it essential to invest in robust protection measures.
Conclusion
The future of cloud computing will be shaped by the rapid adoption of cloudspace technologies, which will redefine how businesses operate. With trends like edge computing, hybrid cloud strategies, and AI integration, companies that embrace these innovations will be well-positioned for success in the digital age.
FAQs, cloudspace technologies
1. What services does Cloudspace Technologies offer for enterprise cloud migration?
Cloudspace Technologies provides a comprehensive suite of cloud migration services, including infrastructure assessment, multi-cloud strategy design, application refactoring, and automated migration tools. They specialize in minimizing downtime during migration while ensuring security, scalability, and cost optimization.
2. How does Cloudspace Technologies ensure data security in cloud environments?
Cloudspace Technologies integrates advanced security protocols such as end-to-end encryption, zero-trust architectures, and AI-driven threat detection into their cloud solutions. They adhere to international compliance standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001, ensuring that client data remains secure both in transit and at rest.
3. What makes Cloudspace Technologies’ multi-cloud management unique?
Cloudspace Technologies offers a unified management platform that enables seamless orchestration and governance across multiple cloud providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud). Their platform includes intelligent automation for workload distribution, real-time performance monitoring, and cost-management tools to optimize cloud usage.
4. How does Cloudspace Technologies handle cloud-native application development?
Cloudspace specializes in building cloud-native applications using microservices architecture, containerization (e.g., Kubernetes, Docker), and serverless computing. They ensure that applications are designed for agility, allowing businesses to scale efficiently while maintaining high availability and performance.
5. What kind of DevOps integration does Cloudspace Technologies provide?
Cloudspace Technologies offers fully integrated DevOps services that streamline CI/CD pipelines, automate testing, and provide continuous monitoring. Their DevOps practices are tightly aligned with cloud infrastructure, ensuring faster time-to-market and improved collaboration between development and operations teams.