Wireless Technology: How to Keep Your Data Secure in 2024

Introduction
As wireless technology continues to advance, it plays a pivotal role in our daily lives—from smartphones and IoT devices to public Wi-Fi and workplace networks. While convenient, wireless technology also opens the door to cyber threats and security vulnerabilities.
With increasing cyberattacks, securing your data when using wireless networks is essential. This article explores how you can protect your information using wireless technology in 2024, covering vital topics like encryption, VPNs, and wireless network protection.
What is Wireless technology?
Wireless technology refers to the transmission of data or power between devices without the use of physical connections, like wires or cables. Instead, it uses electromagnetic waves, such as radio frequencies (RF), infrared (IR), or microwave signals, to communicate over distances.
Here are some key points to understand about wireless technology:
-
Types of Wireless Communication:
- Wi-Fi: Used for local area networks (LAN) and internet access, allowing devices like laptops and smartphones to connect to the internet wirelessly.
- Bluetooth: A short-range wireless technology commonly used to transfer data between devices like phones, headphones, and keyboards.
- Cellular Networks: Mobile communication technology (like 4G, 5G) that allows long-distance communication for mobile phones and other devices.
- NFC (Near Field Communication): Used for short-distance communication, such as contactless payments and file sharing.
- How it Works: Wireless systems use transmitters to send data through the air via electromagnetic waves. Devices with receivers detect these signals and translate them into usable data, such as voice, text, or internet.
- Benefits:
- Mobility: Users can move freely while remaining connected.
- Convenience: No need for cables, making setup and operation easier.
- Scalability: Wireless networks can be expanded easily without physical infrastructure.
- Applications: Wireless technology is found in everything from smartphones and computers to smart home systems, medical devices, and industrial automation.
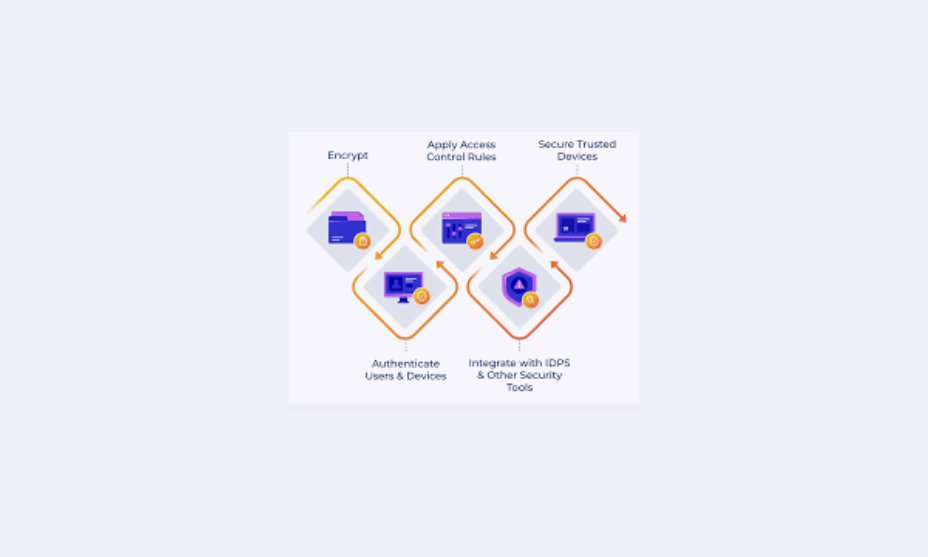
Securing a wireless network is crucial to protecting sensitive information and maintaining privacy. Here are three effective ways to enhance your wireless network’s security:
What are three ways a wireless network can be secured?
Use Strong, Unique Passwords
A strong and unique password is your first line of defense against unauthorized access. Ensure that the password is:
- Complex: Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Lengthy: Aim for at least 12-16 characters.
- Unpredictable: Avoid easily guessable information, such as birthdays or common words. Consider using a password manager to generate and store complex passwords.
Enable WPA3 Encryption
WPA3 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 3) is the latest Wi-Fi encryption protocol that provides stronger security than its predecessors (like WPA2). By enabling WPA3 on your wireless router:
- Enhanced Security: It offers better protection against password guessing attempts and brute-force attacks.
- Individual Data Encryption: WPA3 encrypts each session individually, even on open networks, ensuring that your data remains secure.
- Transitioning: If WPA3 is not available, ensure you use at least WPA2 with a strong password.
Change Default SSID Settings
The default SSID (Service Set Identifier) can give away information about your router and its manufacturer, making it easier for hackers to exploit vulnerabilities. To mitigate this risk:
- Customize the SSID: Change the network name to something unique and non-identifiable, avoiding personal information.
- Hide the SSID: You can choose to hide your SSID, which means it won’t be visible to casual users. However, this can also complicate connecting new devices.
By implementing these strategies, you can significantly improve the security of your wireless network and protect against unauthorized access and potential threats.
Understanding Wireless Technology in 2024
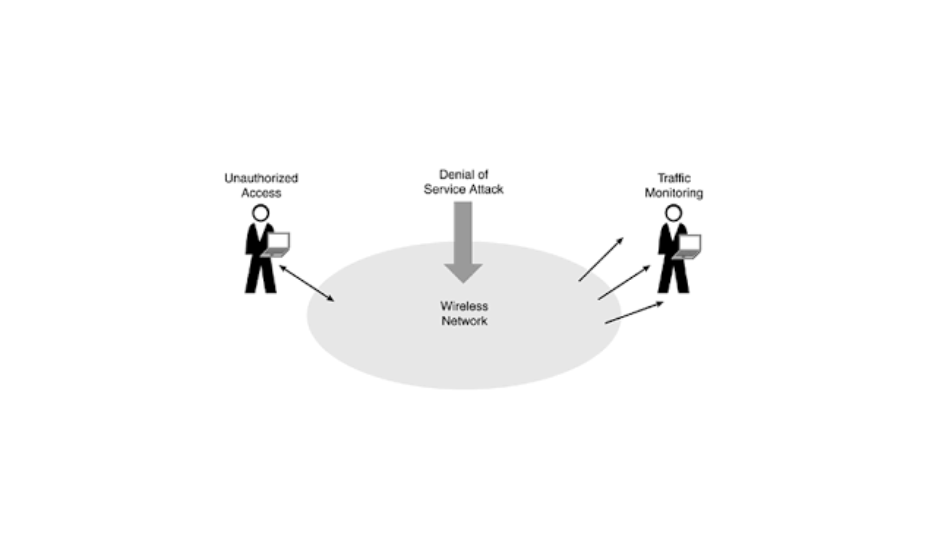
Common Wireless Security Threats
Despite its many benefits, wireless technology is susceptible to a variety of security threats. These include:
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Hackers intercept data being transmitted over a wireless network, posing as legitimate entities.
- Data Interception: Unencrypted wireless communications can be easily intercepted by cybercriminals.
- Malware: Viruses and malicious software can infect devices via unsecured wireless connections.
- Weak Network Security: Using outdated encryption protocols or weak passwords makes your wireless network vulnerable to attacks.
Understanding these threats is the first step in protecting your data on wireless networks.
How Can You Protect Your Information When Using Wireless Technology?
To ensure your data remains secure when using wireless technology, follow these actionable tips:
- Use Strong Passwords: Ensure your Wi-Fi network and devices use strong, unique passwords that are hard to guess.
- Data Encryption: Use WPA3 or WPA2 encryption protocols to protect your wireless network. Encrypt sensitive files before sharing them over Wi-Fi.
- Update Your Software: Regularly update your device software and network hardware to patch vulnerabilities.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Use 2FA to add an extra layer of security when logging into wireless networks or devices.
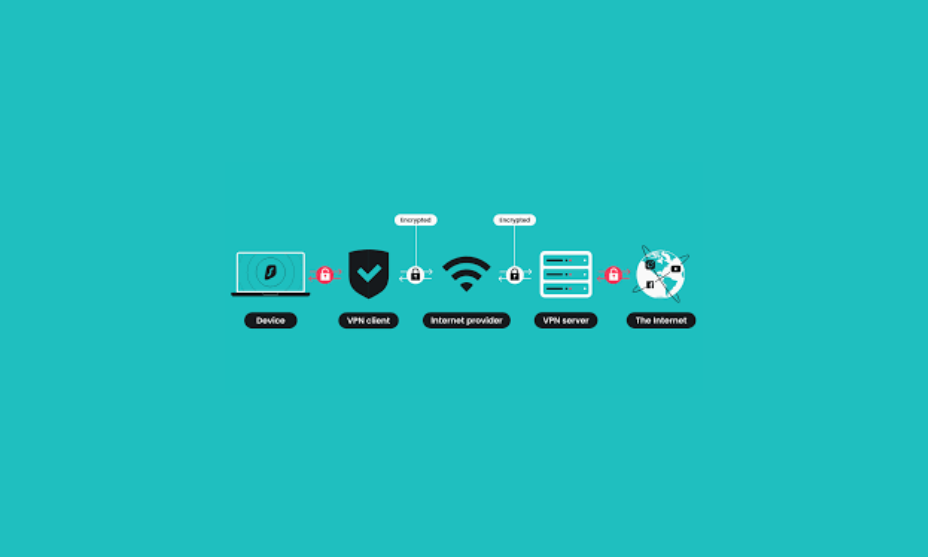
The Importance of Using VPNs on Public Networks
When using public Wi-Fi networks, a Virtual Private Network (VPN) is essential for securing your data. Public networks are notorious for being insecure, allowing hackers to easily intercept unencrypted data. A VPN encrypts your data, preventing malicious actors from accessing your information, even on unsecured Wi-Fi.
Encryption and its Role in Wireless Security
Data encryption plays a critical role in wireless security. Modern encryption standards like WPA3 provide robust protection by scrambling data, making it unreadable to unauthorized users. It’s important to configure your wireless network to use the highest encryption protocol available to ensure maximum protection.
Some key encryption standards include:
- WPA3: The latest wireless encryption standard, offering enhanced security for home and business networks.
- WPA2: A widely used encryption protocol still effective for most users, but slightly less secure than WPA3.
Setting Up a Secure Wireless Network at Home or Work
To secure your home or office wireless network, follow these best practices:
- Use Strong Encryption: Configure your router to use WPA3 encryption.
- Hide Your SSID: Make your wireless network less visible by disabling SSID broadcasting.
- Install a Network Firewall: Firewalls provide an additional layer of defense against unauthorized access.
- Change Default Router Settings: Default settings on routers are often easy targets for attackers. Change your default SSID and password.
- Limit Wireless Access Points (WAP): Ensure only trusted devices are allowed to connect to your network.
Best Practices for Mobile Device Security
Mobile devices are often targets for cyberattacks. To secure your smartphone or tablet:
- Install Security Apps: Use reliable antivirus and anti-malware apps.
- Enable Device Encryption: Most modern smartphones offer encryption options to protect data stored on the device.
- Use Strong Passcodes or Biometrics: Set a strong password or enable fingerprint/face recognition to secure your device.
- Avoid Untrusted Apps: Download apps only from official app stores and avoid third-party sites.
Risks of Using Public Wi-Fi and How to Stay Safe
Public Wi-Fi networks pose several risks, including:
- Data Theft: Hackers can easily intercept unencrypted data on public Wi-Fi.
- Malware Attacks: Cybercriminals can use public networks to distribute malware to connected devices.
To stay safe on public Wi-Fi, follow these guidelines:
- Use a VPN: Always use a VPN to encrypt your data.
- Disable File Sharing: Turn off file sharing features when connected to public networks.
- Avoid Sensitive Transactions: Refrain from accessing banking apps or making purchases on public Wi-Fi.
How IoT Devices Can Compromise Wireless Security
While IoT devices bring convenience, they can also compromise your wireless network’s security if not properly secured. IoT devices like smart cameras, thermostats, and speakers often have weak security features. To protect your network:
- Use Strong Passwords: Set strong, unique passwords for each device.
- Isolate IoT Devices: Create a separate network for IoT devices to prevent them from accessing your primary network.
- Regular Updates: Ensure that IoT devices are regularly updated with the latest security patches.
The Role of Two-Factor Authentication in Securing Wireless Networks
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is an essential layer of protection for wireless networks. With 2FA, even if a hacker steals your password, they won’t be able to access your account without a second form of verification, like a code sent to your phone. This greatly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
How to Secure File Sharing Over Wireless Networks
When sharing files over a wireless network, follow these security practices:
- Encrypt Files: Use encryption tools to protect sensitive files before sharing.
- Password-Protect Shared Files: Always set a password for files shared over wireless networks.
- Use Secure File-Sharing Platforms: Opt for secure file-sharing services that offer end-to-end encryption.
What is WPA3?
WPA3 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 3) is the latest wireless security protocol developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance, designed to provide enhanced protection for wireless networks. It replaces WPA2, the previous security standard, by addressing vulnerabilities and providing stronger encryption and privacy measures. WPA3 was introduced in 2018 to offer better defense against cyber threats and improve the overall security of Wi-Fi networks.
Key Features of WPA3
- Stronger Encryption: WPA3 uses 128-bit encryption for personal networks and 192-bit encryption for enterprise networks. This provides stronger data protection, ensuring that even if data is intercepted, it’s difficult to decrypt.
- Improved Protection Against Brute-Force Attacks: WPA3 protects against dictionary attacks where hackers try multiple password combinations to gain access to the network. The protocol limits the number of guesses an attacker can make before they are locked out, significantly reducing the likelihood of success.
- Forward Secrecy: WPA3 introduces forward secrecy, ensuring that even if an attacker obtains the password of a network, they cannot decrypt previously captured data. This is crucial for maintaining the privacy of past communications.
- Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE): SAE replaces the Pre-Shared Key (PSK) authentication method used in WPA2. This prevents attackers from capturing and analyzing data during the authentication process, offering more secure password-based protection.
- Personalized Data Encryption: In public Wi-Fi networks, WPA3 offers individual encryption for each device, which prevents attackers from snooping on traffic from other connected devices. This feature is especially useful in open networks like coffee shops or airports.
- Easy Connect (for IoT Devices): WPA3 makes it easier and safer to connect Internet of Things (IoT) devices, which often lack a traditional user interface. The new Easy Connect feature allows devices to join the network securely by using a smartphone or other device to scan a QR code.
Why is WPA3 Important for Wireless Security?
- Enhanced Protection for Weak Passwords: WPA3 offers better security even if users set weak or simple passwords. While strong passwords are always recommended, the protocol is more resilient to attacks on weaker passwords compared to WPA2.
- Protection from Eavesdropping: WPA3’s individualized data encryption ensures that even in a shared network, such as public Wi-Fi, each user’s data remains private and secure. This minimizes the risks associated with public networks, making them safer for sensitive transactions.
- Future-Proof Security: With stronger encryption standards and forward secrecy, WPA3 is designed to defend against modern and evolving threats. Its robust security measures ensure that Wi-Fi networks are more secure in the face of increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks.
- Safeguarding IoT Devices: With the growing adoption of smart home devices, WPA3 helps secure these often vulnerable IoT devices, ensuring they don’t become entry points for cybercriminals.
- Regulatory and Industry Standard: WPA3 is becoming the security standard for new devices, and as more routers and devices adopt this protocol, it’s important for users to stay up to date to ensure compatibility and maintain the highest level of security.
How can I maintain the security of my wireless network?
- Modify the name that your home WiFi defaults to.
- Create a strong and distinctive password for your wireless network.
- Turn on network encryption.
- Switch off the broadcasting of the network name.
- Update the software on your router.
- Ensure that your firewall is functioning well.
- To access your network, use a VPN.
How to make Wi-Fi private?
Conclusion:
Wireless technology has transformed the way we live and work, but it comes with its own set of security challenges. By understanding the risks and following best practices—like using strong encryption, VPNs, and 2FA you can protect your data when using wireless technology in 2024. Stay vigilant, keep your devices updated, and take the necessary steps to safeguard your information.
FAQs, Wireless Technology
What is wireless technology?
Wireless technology refers to the transfer of information or power between two or more points that are not connected by physical cables. It uses electromagnetic waves to transmit data and is commonly used in devices like smartphones, laptops, and wireless networks.
How does wireless technology work?
Wireless technology operates through the transmission of radio waves, microwaves, or infrared signals. Data is sent from a transmitter (like a router) to a receiver (like a smartphone) without the need for wired connections, utilizing antennas to facilitate communication.
What are the types of wireless technology?
There are several types of wireless technology, including:Wi-Fi: Allows devices to connect to the internet wirelessly.
Bluetooth: Enables short-range communication between devices.
Cellular networks: Provides mobile communication over large distances.
Satellite communication: Uses satellites to transmit data globally.
Near Field Communication (NFC): Facilitates data exchange over short distances.
What are the advantages of wireless technology?
Wireless technology offers numerous benefits, including:Mobility: Users can access networks and devices without being tethered to cables.
Convenience: Easy to set up and use, with minimal installation requirements.
Scalability: It’s easier to expand networks by adding new devices without extensive wiring.
Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces the need for physical infrastructure and maintenance.
What are the common applications of wireless technology?
Wireless technology is used in various applications, including:Mobile communication: Enabling voice and data services on smartphones.
Internet access: Providing Wi-Fi connectivity in homes, offices, and public spaces.
IoT (Internet of Things): Connecting smart devices for automation and monitoring.
Healthcare: Facilitating remote patient monitoring and telemedicine.